Understand FDA drug label terms like contraindication, precaution, dosage, and drug interactions to use medications safely. Learn what each section means and why it matters for your health.
Drug interactions: what to watch for and what to do
Drug interactions happen when one medicine changes how another works. That can mean a drug becomes stronger, weaker, or more likely to cause side effects. You probably take more than one medicine, or use OTC drugs, supplements, or herbal remedies — so knowing the common risks saves time and trouble.
Common interaction examples you’ll run into
Some combinations pop up often. For example, mixing NSAIDs (like ibuprofen) with blood thinners raises bleeding risk. Grapefruit juice can boost levels of statins and some blood pressure meds by blocking liver enzymes. Combining SSRIs with MAOIs or certain migraine drugs can trigger serotonin syndrome — that’s serious and needs quick medical help. Antibiotics like macrolides and some antifungals can prolong the QT interval, which matters if you already take other QT-prolonging meds.
Antibiotics matter too: trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim) can raise INR when you’re on warfarin and can spike potassium if you use ACE inhibitors or spironolactone. Diuretics such as furosemide can increase ototoxicity risk with aminoglycoside antibiotics and sometimes change lithium levels. Bisphosphonates like Fosamax don’t mix well with calcium supplements at the same time — calcium lowers their absorption.
Kids, the heart, and special flags
Children aren’t small adults. Hydroxyzine, for example, interacts with CNS depressants and drugs that prolong QT — parents should check doses and avoid mixing sedatives or certain heart drugs. Antihistamines like azelastine may have heart effects when combined with other cardiovascular medicines. Always confirm pediatric dosing and interactions with your pediatrician or pharmacist.
Herbal products can be sneaky: St. John’s wort cuts the effectiveness of many meds (including some antidepressants and birth control) by speeding up metabolism. Don’t forget alcohol — it can worsen liver strain with acetaminophen and add sedation with many prescriptions.
Want a quick checklist? Keep a single updated list of everything you take (prescription, OTC, supplements). Use a reliable interaction checker online or ask a pharmacist before starting anything new. Read drug leaflets for key warnings like QT prolongation or contraindicated combinations. If a provider prescribes a drug that worries you, ask about safe alternatives or monitoring plans (blood tests, ECGs, INR checks).
Don’t stop or change doses on your own. If you notice sudden dizziness, breathing trouble, fainting, fast heartbeat, severe nausea, or unexpected bleeding — get medical help right away. For non-urgent questions, a pharmacist is often the fastest person to call.
Bottom line: being proactive beats surprises. Keep one medication list, check before adding OTCs or herbs, and ask a pharmacist or clinician about any risky combos. That small effort keeps your meds working and lowers the chance of dangerous interactions.
Learn how to accurately share your over-the-counter meds and supplement use with your healthcare provider to prevent dangerous interactions. Get practical steps, real examples, and expert-backed advice.
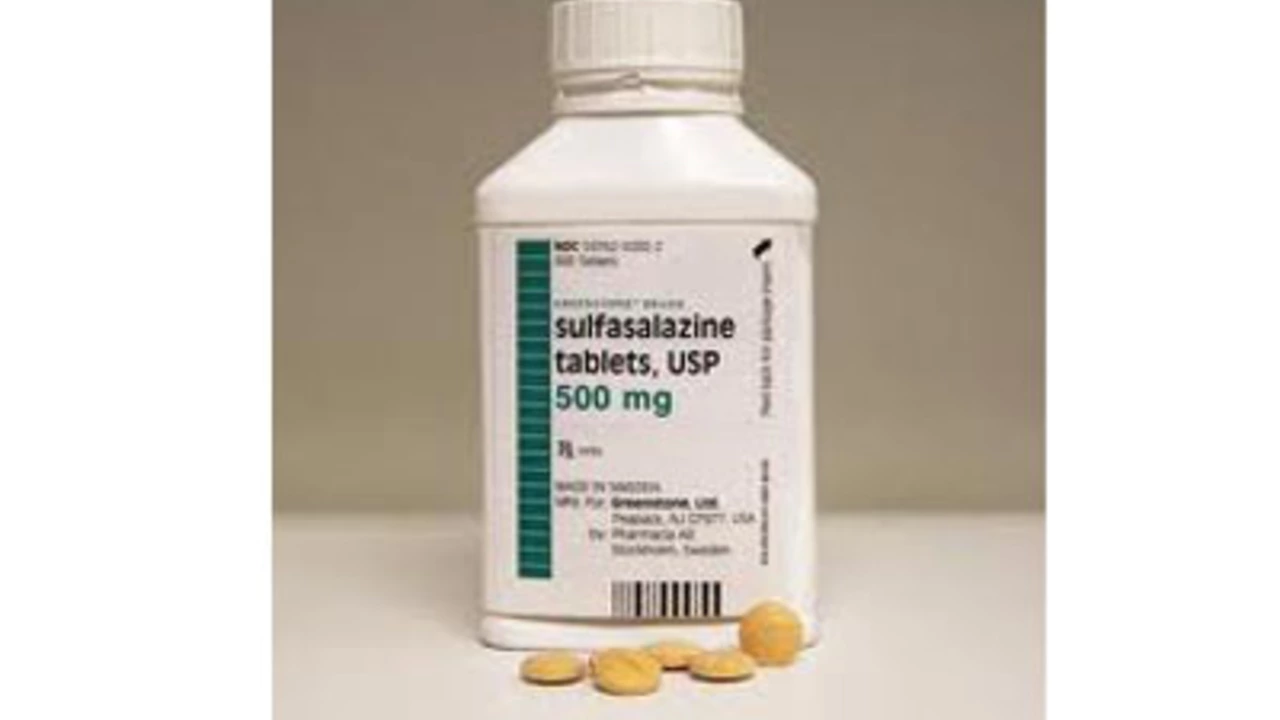
In my latest blog post, I explore the relationship between Sulfasalazine, a common medication for inflammatory conditions, and vaccinations. It's crucial for patients on this medication to understand its potential interactions with vaccines. Some research suggests that Sulfasalazine might lower the effectiveness of certain vaccines. However, it's generally safe to receive vaccines while on this medication, but always discuss it with your healthcare provider. Stay informed and proactive about your health, especially when it involves medications and vaccinations.